チャットボットが「記憶から」回答できない質問を処理するには、web 検索ツールを統合します。チャットボットはこのツールを使用して関連情報を検索してより良い応答を提供します。
LangGraph : Get started : 基本 – Tavily Web 検索ツールの追加
作成 : クラスキャット・セールスインフォメーション
作成日時 : 06/01/2025
* 本記事は langchain-ai.github.io の以下のページを独自に翻訳した上で、補足説明を加えてまとめ直しています :
* サンプルコードの動作確認はしておりますが、必要な場合には適宜、追加改変しています。
* ご自由にリンクを張って頂いてかまいませんが、sales-info@classcat.com までご一報いただけると嬉しいです。
◆ お問合せ : 下記までお願いします。
- クラスキャット セールス・インフォメーション
- sales-info@classcat.com
- ClassCatJP

LangGraph : Get started : 基本 – Tavily Web 検索ツールの追加
チャットボットが「記憶から」回答できない質問を処理するには、web 検索ツールを統合します。チャットボットはこのツールを使用して関連情報を検索してより良い応答を提供します。
前提条件
このチュートリアルを始める前に、次を持っていることを確認してください :
- Tavily 検索エンジン 用の API キー
1.検索エンジンのインストール
Tavily 検索エンジンを使用するために要件をインストールします :
pip install -U langchain-tavily
環境の設定
検索エンジン API キーで環境を設定します :
_set_env("TAVILY_API_KEY")
3. ツールの定義
web 検索ツールの定義 :
API リファレンス: TavilySearch
Tavily 検索 API にクエリーを発行して json を取得するツールです。Tavily の検索 API は AI エージェント (LLM) 向けに特に構築された検索エンジンで、リアルタイムに正確で事実に基づいた結果を高速に提供します。
from langchain_tavily import TavilySearch
tool = TavilySearch(max_results=2)
tools = [tool]
tool.invoke("What's a 'node' in LangGraph?")
結果は、チャットボットが質問に答えるために使用できるページの概要です :
{'query': "What's a 'node' in LangGraph?",
'follow_up_questions': None,
'answer': None,
'images': [],
'results': [{'title': "Introduction to LangGraph: A Beginner's Guide - Medium",
'url': 'https://medium.com/@cplog/introduction-to-langgraph-a-beginners-guide-14f9be027141',
'content': 'Stateful Graph: LangGraph revolves around the concept of a stateful graph, where each node in the graph represents a step in your computation, and the graph maintains a state that is passed around and updated as the computation progresses. LangGraph supports conditional edges, allowing you to dynamically determine the next node to execute based on the current state of the graph. We define nodes for classifying the input, handling greetings, and handling search queries. def classify_input_node(state): LangGraph is a versatile tool for building complex, stateful applications with LLMs. By understanding its core concepts and working through simple examples, beginners can start to leverage its power for their projects. Remember to pay attention to state management, conditional edges, and ensuring there are no dead-end nodes in your graph.',
'score': 0.7065353,
'raw_content': None},
{'title': 'LangGraph Tutorial: What Is LangGraph and How to Use It?',
'url': 'https://www.datacamp.com/tutorial/langgraph-tutorial',
'content': 'LangGraph is a library within the LangChain ecosystem that provides a framework for defining, coordinating, and executing multiple LLM agents (or chains) in a structured and efficient manner. By managing the flow of data and the sequence of operations, LangGraph allows developers to focus on the high-level logic of their applications rather than the intricacies of agent coordination. Whether you need a chatbot that can handle various types of user requests or a multi-agent system that performs complex tasks, LangGraph provides the tools to build exactly what you need. LangGraph significantly simplifies the development of complex LLM applications by providing a structured framework for managing state and coordinating agent interactions.',
'score': 0.5008063,
'raw_content': None}],
'response_time': 1.38}
4. グラフの定義
最初のチュートリアルで作成した StateGraph に対して、LLM に bind_tools を追加します。これは、LLM が検索エンジンを使用したい場合に正しい JSON 形式を認識させます。
最初に LLM を選択しましょう :
OpenAI
pip install -U "langchain[openai]"
import os
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-..."
llm = init_chat_model("openai:gpt-4.1")
Anthropic
import os
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-..."
llm = init_chat_model("openai:gpt-4.1")
import os
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
os.environ["ANTHROPIC_API_KEY"] = "sk-..."
llm = init_chat_model("anthropic:claude-3-5-sonnet-latest")
これでそれを StateGraph に組み込むことができます :
from typing import Annotated
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END
from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages
class State(TypedDict):
messages: Annotated[list, add_messages]
graph_builder = StateGraph(State)
# Modification: tell the LLM which tools it can call
# highlight-next-line
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(tools)
def chatbot(state: State):
return {"messages": [llm_with_tools.invoke(state["messages"])]}
graph_builder.add_node("chatbot", chatbot)
5. ツールを実行する関数の作成
次に、ツールが呼び出された場合に実行する関数を作成します。BasicToolNode のいう名前の新しいノードにツールを追加することでこれを行います、これは状態の最新のメッセージを確認して、メッセージが tool_calls を含むならばツールを呼び出します。それは、LLM の tool_calling に依存しています、これは Anthropic, OpenAI, Google Gemini そしてその他多くの LLM プロバイダーで利用可能す。
API リファレンス: ToolMessage
ツールの実行結果をモデルに返すためのメッセージ。ToolMessage はツール呼び出しの結果を含みます。通常、結果は content フィールド内にエンコードされます。
import json
from langchain_core.messages import ToolMessage
class BasicToolNode:
"""A node that runs the tools requested in the last AIMessage."""
def __init__(self, tools: list) -> None:
self.tools_by_name = {tool.name: tool for tool in tools}
def __call__(self, inputs: dict):
if messages := inputs.get("messages", []):
message = messages[-1]
else:
raise ValueError("No message found in input")
outputs = []
for tool_call in message.tool_calls:
tool_result = self.tools_by_name[tool_call["name"]].invoke(
tool_call["args"]
)
outputs.append(
ToolMessage(
content=json.dumps(tool_result),
name=tool_call["name"],
tool_call_id=tool_call["id"],
)
)
return {"messages": outputs}
tool_node = BasicToolNode(tools=[tool])
graph_builder.add_node("tools", tool_node)
Note : If you do not want to build this yourself in the future, you can use LangGraph’s prebuilt ToolNode.
6. conditional_edges の定義
ツールノードを追加したら、conditional_edges を定義できます。
エッジ は制御フローを一つのノードから次のノードへと導きます。条件付きエッジ は単一のノードから始まり、通常は “if” ステートメントを含み、現在のグラフ状態により異なるノードへ導かれます。これらの関数は現在のグラフ状態を受け取り、どのノードを次に呼び出すかを示す文字列または文字列のリストを返します。
次に、route_tools と呼ばれるルーター関数を定義します、これはチャットボットの出力内の tool_calls をチェックします。add_conditional_edges を呼び出すことでこの関数をグラフに提供します、これはグラフに、チャットボット・ノードが完了したら、この関数を確認して次にどこへ進むか確認するように指示します。
この条件は、ツール呼び出しが存在する場合には tools に、そうでないなら END にルーティングされます。条件は END を返すことができるので、今回は明示的に finish_point を設定する必要はありません。
def route_tools(
state: State,
):
"""
Use in the conditional_edge to route to the ToolNode if the last message
has tool calls. Otherwise, route to the end.
"""
if isinstance(state, list):
ai_message = state[-1]
elif messages := state.get("messages", []):
ai_message = messages[-1]
else:
raise ValueError(f"No messages found in input state to tool_edge: {state}")
if hasattr(ai_message, "tool_calls") and len(ai_message.tool_calls) > 0:
return "tools"
return END
# The `tools_condition` function returns "tools" if the chatbot asks to use a tool, and "END" if
# it is fine directly responding. This conditional routing defines the main agent loop.
graph_builder.add_conditional_edges(
"chatbot",
route_tools,
# The following dictionary lets you tell the graph to interpret the condition's outputs as a specific node
# It defaults to the identity function, but if you
# want to use a node named something else apart from "tools",
# You can update the value of the dictionary to something else
# e.g., "tools": "my_tools"
{"tools": "tools", END: END},
)
# Any time a tool is called, we return to the chatbot to decide the next step
graph_builder.add_edge("tools", "chatbot")
graph_builder.add_edge(START, "chatbot")
graph = graph_builder.compile()
Note : You can replace this with the prebuilt tools_condition to be more concise.
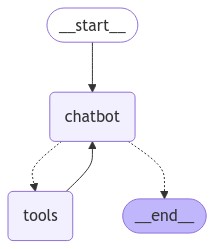
7. グラフの可視化 (オプション)
get_graph メソッドと draw_ascii や draw_png のような “draw” メソッドの一つを使用してグラフを可視化できます。それぞれの draw メソッドは追加の依存関係が必要です。
from IPython.display import Image, display
try:
display(Image(graph.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png()))
except Exception:
# This requires some extra dependencies and is optional
pass
8. ボットに質問する
これで、チャットボットにトレーニングデータ以外の質問をすることができます :
def stream_graph_updates(user_input: str):
for event in graph.stream({"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": user_input}]}):
for value in event.values():
print("Assistant:", value["messages"][-1].content)
while True:
try:
user_input = input("User: ")
if user_input.lower() in ["quit", "exit", "q"]:
print("Goodbye!")
break
stream_graph_updates(user_input)
except:
# fallback if input() is not available
user_input = "What do you know about LangGraph?"
print("User: " + user_input)
stream_graph_updates(user_input)
break
Assistant: [{'text': "To provide you with accurate and up-to-date information about LangGraph, I'll need to search for the latest details. Let me do that for you.", 'type': 'text'}, {'id': 'toolu_01Q588CszHaSvvP2MxRq9zRD', 'input': {'query': 'LangGraph AI tool information'}, 'name': 'tavily_search_results_json', 'type': 'tool_use'}]
Assistant: [{"url": "https://www.langchain.com/langgraph", "content": "LangGraph sets the foundation for how we can build and scale AI workloads \u2014 from conversational agents, complex task automation, to custom LLM-backed experiences that 'just work'. The next chapter in building complex production-ready features with LLMs is agentic, and with LangGraph and LangSmith, LangChain delivers an out-of-the-box solution ..."}, {"url": "https://github.com/langchain-ai/langgraph", "content": "Overview. LangGraph is a library for building stateful, multi-actor applications with LLMs, used to create agent and multi-agent workflows. Compared to other LLM frameworks, it offers these core benefits: cycles, controllability, and persistence. LangGraph allows you to define flows that involve cycles, essential for most agentic architectures ..."}]
Assistant: Based on the search results, I can provide you with information about LangGraph:
1. Purpose:
LangGraph is a library designed for building stateful, multi-actor applications with Large Language Models (LLMs). It's particularly useful for creating agent and multi-agent workflows.
2. Developer:
LangGraph is developed by LangChain, a company known for its tools and frameworks in the AI and LLM space.
3. Key Features:
- Cycles: LangGraph allows the definition of flows that involve cycles, which is essential for most agentic architectures.
- Controllability: It offers enhanced control over the application flow.
- Persistence: The library provides ways to maintain state and persistence in LLM-based applications.
4. Use Cases:
LangGraph can be used for various applications, including:
- Conversational agents
- Complex task automation
- Custom LLM-backed experiences
5. Integration:
LangGraph works in conjunction with LangSmith, another tool by LangChain, to provide an out-of-the-box solution for building complex, production-ready features with LLMs.
6. Significance:
...
LangGraph is noted to offer unique benefits compared to other LLM frameworks, particularly in its ability to handle cycles, provide controllability, and maintain persistence.
LangGraph appears to be a significant tool in the evolving landscape of LLM-based application development, offering developers new ways to create more complex, stateful, and interactive AI systems.
Goodbye!
Output is truncated. View as a scrollable element or open in a text editor. Adjust cell output settings...
9. prebuilts の使用
使いやすさのために、以下を LangGraph の prebuilts (事前構築済みコンポーネント) に置き換えるようにコードを調整してください。これらは並列 API 実行のような機能が組み込まれています。
- BasicToolNode は prebuilt ToolNode で置き換えられます
最後の AIMessage 内で呼び出されたツールを実行するノード。
- route_tools は prebuilt tools_condition で置き換えられます
conditional_edge 内で使用して、最後のメッセージが tool 呼び出しを含む場合に ToolNode にルーティングします。そうでないなら、end にルーティングします。
OpenAI
pip install -U "langchain[openai]"
import os
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-..."
llm = init_chat_model("openai:gpt-4.1")
Anthropic
pip install -U "langchain[anthropic]"
import os
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
os.environ["ANTHROPIC_API_KEY"] = "sk-..."
llm = init_chat_model("anthropic:claude-3-5-sonnet-latest")
from typing import Annotated
from langchain_tavily import TavilySearch
from langchain_core.messages import BaseMessage
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END
from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages
from langgraph.prebuilt import ToolNode, tools_condition
class State(TypedDict):
messages: Annotated[list, add_messages]
graph_builder = StateGraph(State)
tool = TavilySearch(max_results=2)
tools = [tool]
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(tools)
def chatbot(state: State):
return {"messages": [llm_with_tools.invoke(state["messages"])]}
graph_builder.add_node("chatbot", chatbot)
tool_node = ToolNode(tools=[tool])
graph_builder.add_node("tools", tool_node)
graph_builder.add_conditional_edges(
"chatbot",
tools_condition,
)
# Any time a tool is called, we return to the chatbot to decide the next step
graph_builder.add_edge("tools", "chatbot")
graph_builder.add_edge(START, "chatbot")
graph = graph_builder.compile()
Congratulations! You’ve created a conversational agent in LangGraph that can use a search engine to retrieve updated information when needed. Now it can handle a wider range of user queries. To inspect all the steps your agent just took, check out this LangSmith trace.
以上
