エージェントは言語モデルをツールと組み合わせて、タスクについて推論し、どのツールを使用するか決定し、解決に向けて繰り返し作業することができるシステムを作成します。
create_agent() は、論文 ReAct: Synergizing Reasoning and Acting in Language Models に基づいた ReAct (Reasoning + Acting) エージェントの実装を提供します。
LangChain 1.0 alpha : コアコンポーネント – エージェント
作成 : クラスキャット・セールスインフォメーション
作成日時 : 09/21/2025
バージョン : 1.0.0a5
* 本記事は docs.langchain.com の以下のページを独自に翻訳した上で、補足説明を加えてまとめ直しています。スニペットはできる限り日本語を使用しています :
* サンプルコードの動作確認はしておりますが、必要な場合には適宜、追加改変しています。
* ご自由にリンクを張って頂いてかまいませんが、sales-info@classcat.com までご一報いただけると嬉しいです。
◆ お問合せ : 下記までお願いします。
- クラスキャット セールス・インフォメーション
- sales-info@classcat.com
- ClassCatJP
LangChain 1.0 alpha : コアコンポーネント – エージェント
エージェントは言語モデルをツールと組み合わせて、タスクについて推論し、どのツールを使用するか決定し、解決に向けて繰り返し作業することができるシステムを作成します。
create_agent() は、論文 ReAct: Synergizing Reasoning and Acting in Language Models に基づいた ReAct (Reasoning + Acting) エージェントの実装を提供します。
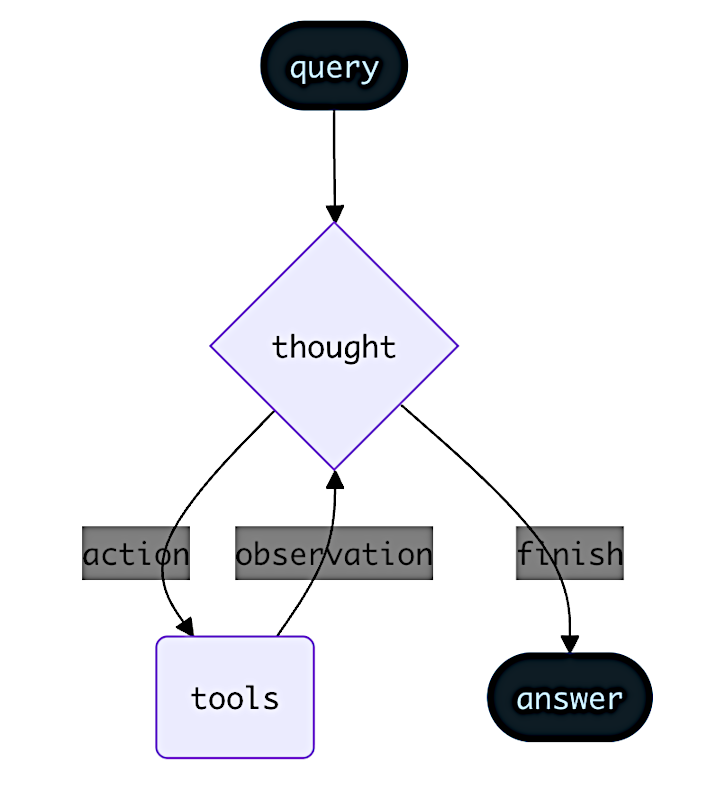
ReAct はエージェントの動作を、思考 (thought) -> 行動 (action) -> 観察 (observation) のステップとして捉えます、そこではモデルは推論を書き出し、ツールを選択し、ツールの結果を確認し、そしてそれを繰り返します。ReAct はハルシネーションを減らし、意思決定プロセスを監査できます : エージェントは仮説を立て (思考)、ツールで検証し (行動)、フィードバックに基づいて計画をアップデートします (観察)。
ReAct ループは停止条件まで実行されます – i.e., モデルが最終的な答えを出力したり、最大反復回数の制限に達した場合です。
Info
create_agent() は LangGraph を使用して、グラフ ベースのエージェント・ランタイムを構築します。グラフは、エージェントが情報を処理する方法を定義する、ノード (ステップ) とエッジ (接続) から構成されます。エージェントはこのグラフ内を移動し、(モデルを呼び出す) モデルノード、(ツールを実行する) ツールノード、pre/post モデル・フック・ノードのようなノードを実行します。Learn more about the graph API.
コア・コンポーネント
モデル
モデル はエージェントの推論エンジンです。モデルは複数の方法で指定できて、静的なモデルと動的なモデルの選択の両方をサポートします。
静的モデル
静的モデルはエージェントを作成する際に一度だけ構成設定され、実行中に変更されません。これは最も一般的で分かりやすいアプローチです。モデル識別子文字列で静的モデルを初期化します :
from langchain.agents import create_agent
agent = create_agent(
"openai:gpt-5",
tools=tools
)
モデル識別子文字列は形式 provider:model (e.g. “openai:gpt-5”) を使用し、自動推論をサポートします (e.g. “gpt-5” は “openai:gpt-5” として推論されます)。モデル構成設定をより細かく制御したい場合には、プロバイダー・パッケージを使用してモデルインスタンスを直接初期化できます :
from langchain.agents import create_agent
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
model = ChatOpenAI(
model="gpt-5",
temperature=0.1,
max_tokens=1000,
timeout=30
)
agent = create_agent(model, tools=tools)
モデル・インスタンスは設定を完全に制御できます。temperature, 最大トークン数、タイムアウトのような特定のパラメータや、configurable API キー、ベース URL、その他のプロバイダー固有の設定をセットする必要がある場合に、それらを使用します。Refer to the API reference to see available params and methods on your model.
動的モデル
動的モデルは、現在の状態とコンテキストに基づいて、実行時に選択されます。これは洗練されたルーティング・ロジックとコストの最適化を可能にします。
動的モデルを使用するには、グラフ状態とランタイム (実行環境) を受け取り、.bind_tools(tools) を使用してバインドされたツールを備えた BaseChatModel のインスタンスを返す関数を提供する必要があります。ここで、tools は tools パラメータのサブセットです。
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.agents import create_agent, AgentState
from langgraph.runtime import Runtime
def select_model(state: AgentState, runtime: Runtime) -> ChatOpenAI:
"""Choose model based on conversation complexity."""
messages = state["messages"]
message_count = len(messages)
if message_count < 10:
return ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4.1-mini").bind_tools(tools)
else:
return ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-5").bind_tools(tools) # Better model for longer conversations
agent = create_agent(select_model, tools=tools)
ツール
ツールはエージェントにアクションを行う機能を与えます。エージェントは、単純なモデルのみのツール・バインディングを超えて、以下を提供します :
- 単一のプロンプトでトリガーされる、一連の複数のツール呼び出し
- 適切な場合のツールの並列呼び出し
- 結果に基づく、動的なツール選択
- ツール再試行ロジックとエラー処理
- ツール呼び出しにわたる状態の永続化
ツールは、次のいずれかとして、エージェントに提供されます :
- ツールのリスト (LangChain @tool、callable (呼び出し可能オブジェクト)、あるいは組み込みプロバイダーツールを表す辞書)
- 構成設定済みの ToolNode
ツールのリストを渡す
ツールのリストをエージェントに渡すと、内部的には ToolNode が作成されます。これは、ツール呼び出しエージェントをセットアップする最も単純な方法です :
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from langchain.agents import create_agent
@tool
def search(query: str) -> str:
"""Search for information."""
return f"Results for: {query}"
@tool
def calculate(expression: str) -> str:
"""Perform calculations."""
return str(eval(expression))
agent = create_agent(model, tools=[search, calculate])
空のツールリストが提供される場合、エージェントはツール呼び出しなしの単一の LLM ノードからなります。
構成設定済みの ToolNode を渡す
代わりに、ToolNode を直接作成してそれをエージェントに渡すこともできます。これは、ツールエラーの処理のような、ツールノードの動作をカスタマイズすることを可能にします :
tool_node = ToolNode(
tools=[search, calculate],
handle_tool_errors="Please check your input and try again."
)
agent = create_agent(model, tools=tool_node)
result = agent.invoke({"messages": [...]})
ToolNode 内でエラーが発生した場合、エージェントはカスタム・エラー・メッセージを含む ToolMessage をモデルに返します :
# result["messages"]
[
...
ToolMessage(content="Please check your input and try again.", tool_call_id="..."),
...
]
Note : To learn more about error handling in ToolNode, see ToolNode.
ReAct ループ内のツール使用
エージェントは ReAct (Reasoning + Acting) パターンに従い、簡潔な推論ステップと対象となるツール呼び出しを交互に行い、そして最終的な答えを提供できるまで、結果に対する観察を続く意思決定にフィードしていきます。
ReAct ループの例
Prompt: Identify the current most popular wireless headphones and verify availability.
================================ Human Message =================================
Find the most popular wireless headphones right now and check if they're in stock
Reasoning: “Popularity is time-sensitive, I need to use the provided search tool.”
Acting: Call search_products("wireless headphones")
================================== Ai Message ==================================
Tool Calls:
search_products (call_abc123)
Call ID: call_abc123
Args:
query: wireless headphones
================================= Tool Message =================================
Found 5 products matching "wireless headphones". Top 5 results: WH-1000XM5, ...
================================== Ai Message ==================================
Tool Calls:
check_inventory (call_def456)
Call ID: call_def456
Args:
product_id: WH-1000XM5
================================== Ai Message ==================================
Tool Calls:
check_inventory (call_def456)
Call ID: call_def456
Args:
product_id: WH-1000XM5
================================= Tool Message =================================
Product WH-1000XM5: 10 units in stock
Reasoning: “I have the most popular model and its stock status. I can now answer the user’s question.”
Acting: Produce final answer
================================== Ai Message ==================================
I found wireless headphones (model WH-1000XM5) with 10 units in stock...
Note : To learn more about tools, see Tools.
プロンプト
プロンプトを提供することで、エージェントがタスクにアプローチする方法を形成できます。prompt パラメータは文字列、SystemMessage や呼び出し可能オブジェクトとして提供できます :
文字列
agent = create_agent(
model,
tools,
prompt="You are a helpful assistant. Be concise and accurate."
)
SystemMessage
agent = create_agent(
model,
tools,
prompt=SystemMessage(content="You are a research assistant. Cite your sources.")
)
呼び出し可能オブジェクト
def dynamic_prompt(state):
user_type = state.get("user_type", "standard")
system_msg = SystemMessage(
content="Provide detailed technical responses."
if user_type == "expert"
else "Provide simple, clear explanations."
)
return [system_msg] + state["messages"]
agent = create_agent(model, tools, prompt=dynamic_prompt)
プロンプトが提供されない場合、エージェントはメッセージから直接、タスクを推測します (infer)。
Note : For more details on message types and formatting, see Messages.
高度な構成設定
構造化出力
ある状況では、エージェントに特定の形式で出力を返すことを望む場合があります。LangChain は、response_format パラメータを使用してこれを行う単純で汎用的な方法を提供します。
from pydantic import BaseModel
from langchain.agents import create_agent
class ContactInfo(BaseModel):
name: str
email: str
phone: str
agent = create_agent(
model,
tools=[search_tool],
response_format=ContactInfo
)
result = agent.invoke({
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Extract contact info from: John Doe, john@example.com, (555) 123-4567"}]
})
result["structured_response"]
# ContactInfo(name='John Doe', email='john@example.com', phone='(555) 123-4567')
Note : To learn about structured output, see Structured output.
メモリ
エージェントはメッセージ状態を通して、会話履歴を自動的に保持します。また、会話中に追加情報を記憶するために、エージェントを構成設定してカスタム状態スキーマを使用することもできます。
状態に保存された情報はエージェントの 短期メモリ として考えることができます :
from typing import TypedDict
from typing_extensions import Annotated
from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages
from langchain.agents import create_agent
from langchain.agents import AgentState
class CustomAgentState(AgentState):
messages: Annotated[list, add_messages]
user_preferences: dict
agent = create_agent(
model,
tools=tools,
state_schema=CustomAgentState
)
# The agent can now track additional state beyond messages. This custom state can be accessed and updated throughout the conversation.
result = agent.invoke({
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "I prefer technical explanations"}],
"user_preferences": {"style": "technical", "verbosity": "detailed"},
})
Note : To learn more about memory, see Memory. For information on implementing long-term memory that persists across sessions, see Long-term memory.
ストリーミング
最終的なレスポンスを取得するために .invoke を使用してエージェントが呼び出せる方法を見てきました。エージェントが複数のステップを実行する場合、時間がかかる場合があります。中間的な進捗を表示するため、発生したメッセージをストリーミングで返すことができます。
for chunk in agent.stream({
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Search for AI news and summarize the findings"}]
}, stream_mode="values"):
# Each chunk contains the full state at that point
latest_message = chunk["messages"][-1]
if latest_message.content:
print(f"Agent: {latest_message.content}")
elif latest_message.tool_calls:
print(f"Calling tools: {[tc['name'] for tc in latest_message.tool_calls]}")
Note : For more details on streaming, see Streaming.
以上
