Human in the Loop (HITL) は、AG2 エージェントがワークフロー内で人間と協調することを可能にする強力なパターンです。すべての決定を独自に行う代わりに、エージェントは重要な決定ポイントで人間のオペレータに確認し、AI の効率性を人間の判断と組み合わせることができます。
AG2 : ユーザガイド – 基本概念 : Human in the Loop
作成 : クラスキャット・セールスインフォメーション
作成日時 : 09/02/2025
バージョン : v0.9.9
* 本記事は docs.ag2.ai の以下のページを独自に翻訳した上でまとめ直し、補足説明を加えています :
* サンプルコードの動作確認はしておりますが、必要な場合には適宜、追加改変しています。
* ご自由にリンクを張って頂いてかまいませんが、sales-info@classcat.com までご一報いただけると嬉しいです。
◆ お問合せ : 下記までお願いします。
- クラスキャット セールス・インフォメーション
- sales-info@classcat.com
- ClassCatJP
AG2 : ユーザガイド – 基本概念 : Human in the Loop
Human in the Loop (HITL) は、AG2 エージェントがワークフロー内で人間と協調することを可能にする強力なパターンです。すべての決定を独自に行う代わりに、エージェントは重要な決定ポイントで人間のオペレータに確認し、AI の効率性を人間の判断と組み合わせることができます。
HITL のアナロジー
Human in the Loop を病院の治療システムのように考えてみましょう :
- 医師 (AI エージェント) は患者を診察し、検査を行い、そして治療計画を準備します。
- 重篤で異常な病状については、進める前にシニア専門家 (人間) に相談します。
- 専門家は重要な治療や異常なケースについて最終的な承認を提供します。
- 承認されれば、医師はすべての詳細を処理します。
- このパートナーシップは、重要な決定のために医師の効率性を専門家の判断と組み合わせます。
このアプローチは、重要な決定が適切な監視を受ける一方で、ルーチンケースは素早く処理されることを保証します。
When to Use HITL
Human in the Loop は以下の場合に特に有益です :
- 意思決定が繊細な判断を必要とする (e.g. 金融コンプライアンス、法務関連事項)
- エラーが重大な結果となる可能性がある場合 (e.g., 金融取引き、安全性が重要な (safety-critical) システム)
- プロセスが主観的な入力 (e.g., コンテンツの承認、デザインの選択) から恩恵を受ける場合
- 規制要件が人間の監視を義務付けている (e.g. 金融サービス、ヘルスケア)
AG2 での HITL の実装
AG2 で Human in the Loop ワークフローを作成するのは ConversableAgent を使用すれば簡単です、ConversableAgent ではエージェントは human_input_mode パラメータで制御される、human in the loop となります :
from autogen import ConversableAgent
# Create a human agent that will always prompt for input
human = ConversableAgent(
name="human",
human_input_mode="ALWAYS", # Always ask for human input
)
# Create an AI agent that never asks for human input directly
ai_agent = ConversableAgent(
name="ai_assistant",
system_message="You are a helpful AI assistant",
human_input_mode="NEVER", # Never ask for human input directly
)
human_input_mode パラメータには 3 つの取りうる値があります :
- ALWAYS : エージェントは人間の入力を応答として使用します。
- TERMINATE : エージェントは、会話を終了するときだけ、入力を要求します。
- NEVER : エージェントは人間の入力を決して求めません。
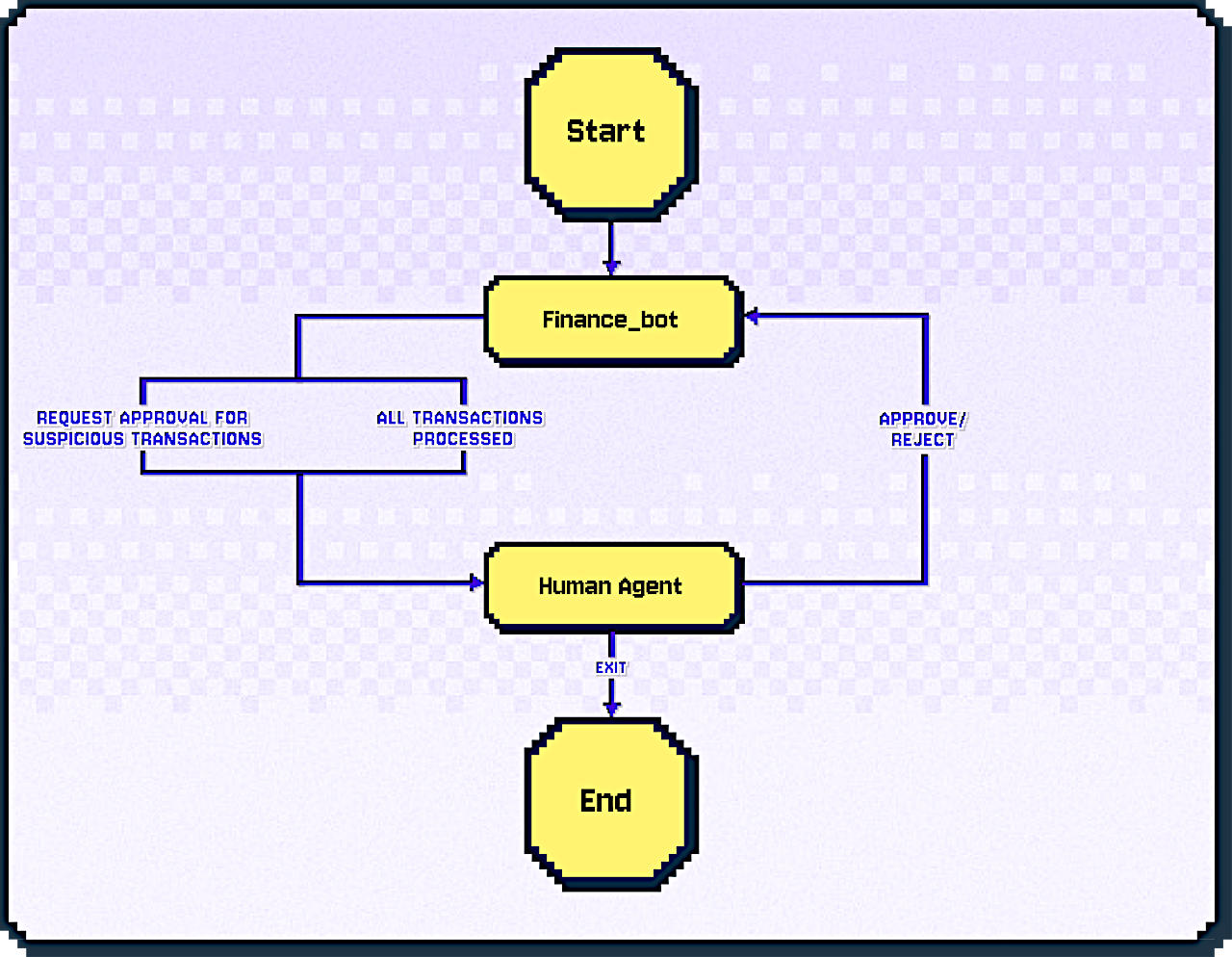
財務コンプライアンスの例
取引きを自動的にレビューし、疑わしいものには人間のレビューのためのフラグを立てる財務コンプライアンス・システムを構築しましょう。この例は、前のセクションからの基本的な ConversableAgent の上に 2 つの重要な改良を備えて構築されます :
- 洗練された指示 : 疑わしい取引きについて質問に答えるだけではなく、財務ボットは特定の基準により積極的に識別して、処理します。
- 人間の入力モード : human_input_mode=”ALWAYS” の設定は、ワークフローを続行する前に人間が入力する必要がある、チェックポイントを作成します – これは規則順守に不可欠です。
ワークフローは次のパターンに従います :

財務エージェントとヒューマンエージェントの確立
from autogen import ConversableAgent, LLMConfig
import os
import random
# Note: Make sure to set your API key in your environment first
# Configure the LLM
llm_config = LLMConfig(
api_type="openai",
model="gpt-4o-mini",
api_key=os.environ.get("OPENAI_API_KEY"),
temperature=0.2,
)
# Define the system message for our finance bot
finance_system_message = """
You are a financial compliance assistant. You will be given a set of transaction descriptions.
For each transaction:
- If it seems suspicious (e.g., amount > $10,000, vendor is unusual, memo is vague), ask the human agent for approval.
- Otherwise, approve it automatically.
Provide the full set of transactions to approve at one time.
If the human gives a general approval, it applies to all transactions requiring approval.
When all transactions are processed, summarize the results and say "You can type exit to finish".
"""
# Create the finance agent with LLM intelligence
with llm_config:
finance_bot = ConversableAgent(
name="finance_bot",
system_message=finance_system_message,
)
# Create the human agent for oversight
human = ConversableAgent(
name="human",
human_input_mode="ALWAYS", # Always ask for human input
)
human-in-the-loop なしでは、財務ボットは疑わしい取引きを誤って承認する可能性があります。HITL では、必要に応じて人間の判断が的確に介入する、重要な安全メカニズムを作成します。
会話の開始
幾つかのサンプル取引きを生成して、エージェント間の会話を開始しましょう :
# Generate sample transactions - this creates different transactions each time you run
VENDORS = ["Staples", "Acme Corp", "CyberSins Ltd", "Initech", "Globex", "Unicorn LLC"]
MEMOS = ["Quarterly supplies", "Confidential", "NDA services", "Routine payment", "Urgent request", "Reimbursement"]
def generate_transaction():
amount = random.choice([500, 1500, 9999, 12000, 23000, 4000])
vendor = random.choice(VENDORS)
memo = random.choice(MEMOS)
return f"Transaction: ${amount} to {vendor}. Memo: {memo}."
# Generate 3 random transactions
transactions = [generate_transaction() for _ in range(3)]
# Format the initial message
initial_prompt = (
"Please process the following transactions one at a time:\n\n" +
"\n".join([f"{i+1}. {tx}" for i, tx in enumerate(transactions)])
)
# Start the conversation from the human agent
response = human.run(
recipient=finance_bot,
message=initial_prompt,
)
# Display the response
response.process()
実行中に何が起きるか
このコードを実行すると :
- 財務ボットは取引きのリストを受け取ります。
- 各取引きを分析してそれが疑わしいか判断します :
- $10,000 を超える総額は疑わしいとフラグ立てされます。
- (“Confidential” のような) 曖昧なメモはレビューのトリガーになる可能性があります。
- 通常の取引きは (少額、馴染みあるベンダー) 自動的に承認されます。
- すべての疑わしい取引きは収集され、承認のために人間に直ちに提示されます。
- 人間が承認をもって応答すると、財務ボットはすべてのフラグ立てされた取引きを処理します。
- 財務ボットはすべての取引きの概要を提供し、ユーザが “exit” とタイプして終了できることを示します。
- 人間は “exit” とタイプして会話を終了します。
完全なコード例
財務コンプライアンスの Human in the Loop の例の完全な、すぐに実行できるコードを以下に示します。これを Python ファイルにコピー&ペーストして、実行して実際にインタラクションを確認できます :
from autogen import ConversableAgent, LLMConfig
import os
import random
# Note: Make sure to set your API key in your environment first
# Configure the LLM
llm_config = LLMConfig(
api_type="openai",
model="gpt-4o-mini",
api_key=os.environ.get("OPENAI_API_KEY"),
temperature=0.2,
)
# Define the system message for our finance bot
finance_system_message = """
You are a financial compliance assistant. You will be given a set of transaction descriptions.
For each transaction:
- If it seems suspicious (e.g., amount > $10,000, vendor is unusual, memo is vague), ask the human agent for approval.
- Otherwise, approve it automatically.
Provide the full set of transactions to approve at one time.
If the human gives a general approval, it applies to all transactions requiring approval.
When all transactions are processed, summarize the results and say "You can type exit to finish".
"""
# Create the finance agent with LLM intelligence
with llm_config:
finance_bot = ConversableAgent(
name="finance_bot",
system_message=finance_system_message,
)
# Create the human agent for oversight
human = ConversableAgent(
name="human",
human_input_mode="ALWAYS", # Always ask for human input
)
# Generate sample transactions - this creates different transactions each time you run
VENDORS = ["Staples", "Acme Corp", "CyberSins Ltd", "Initech", "Globex", "Unicorn LLC"]
MEMOS = ["Quarterly supplies", "Confidential", "NDA services", "Routine payment", "Urgent request", "Reimbursement"]
def generate_transaction():
amount = random.choice([500, 1500, 9999, 12000, 23000, 4000])
vendor = random.choice(VENDORS)
memo = random.choice(MEMOS)
return f"Transaction: ${amount} to {vendor}. Memo: {memo}."
# Generate 3 random transactions
transactions = [generate_transaction() for _ in range(3)]
# Format the initial message
initial_prompt = (
"Please process the following transactions one at a time:\n\n" +
"\n".join([f"{i+1}. {tx}" for i, tx in enumerate(transactions)])
)
# Start the conversation from the human agent
response = human.run(
recipient=finance_bot,
message=initial_prompt,
)
# Display the response
response.process()
出力例
このコードを実行すると、財務ボットが各取引きを分析するのがわかるでしょう。
疑わしい取引きについては、入力を提供することを促されます – approve (承認), deny (拒否), または provide reasoning (理由の提供) のいずれかを入力します。
通常の取引きについては、財務ボットは自動的に承認します。最後に、処理されたすべての取引きの概要レポートが表示されます。
human (to finance_bot): Please process the following transactions one at a time: 1. Transaction: $1500 to Unicorn LLC. Memo: Quarterly supplies. 2. Transaction: $12000 to Acme Corp. Memo: Reimbursement. 3. Transaction: $4000 to CyberSins Ltd. Memo: Routine payment. -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- >>>>>>>> USING AUTO REPLY... finance_bot (to human): Here are the transactions to process: 1. Transaction: $1500 to Unicorn LLC. Memo: Quarterly supplies. - **Approved automatically.** 2. Transaction: $12000 to Acme Corp. Memo: Reimbursement. - **Requires approval.** 3. Transaction: $4000 to CyberSins Ltd. Memo: Routine payment. - **Approved automatically.** Please provide approval for the transaction requiring it. -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Replying as human. Provide feedback to finance_bot. Press enter to skip and use auto-reply, or type 'exit' to end the conversation: approve human (to finance_bot): approve -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- >>>>>>>> USING AUTO REPLY... finance_bot (to human): All transactions have been processed: 1. Transaction: $1500 to Unicorn LLC. Memo: Quarterly supplies. - Approved. 2. Transaction: $12000 to Acme Corp. Memo: Reimbursement. - Approved. 3. Transaction: $4000 to CyberSins Ltd. Memo: Routine payment. - Approved. You can type exit to finish. -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Replying as human. Provide feedback to finance_bot. Press enter to skip and use auto-reply, or type 'exit' to end the conversation: exit >>>>>>>> TERMINATING RUN (e7d81dde-89ff-4cfc-bfd5-26285f5100d0): User requested to end the conversation
以上
